Welcome to your corner of Spanish! In today’s post, we’re going to talk about the pretérito imperfecto tense in Spanish.
The Pretérito imperfecto is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in Spanish to discuss the past. Unlike the pretérito perfecto tense that emphasizes a completed action in the past, the pretérito imperfecto focuses on actions that were habitual, continuous, or actions in progress interrupted by another event (expressed in the pretérito indefinido). It’s like opening a window to the past and observing what was happening at a specific moment.
Uses of the Pretérito Imperfecto:
- Habitual actions: Actions repeated in the past, describing actions that used to occur regularly in the past. For example: Yo siempre jugaba al fútbol los sábados.
- Descriptions in the past: The imperfect past tense is used to describe situations, places, or people in the past. For example: El sol brillaba y hacía calor.
- Actions that occurred in the past, but the exact starting and ending points are unknown: For example: Cuando iba a la universidad, estudiaba todos los días en la biblioteca. “Cuando iba a la universidad” is a moment in the past with uncertain starting and ending points).
- Expressing actions that were ongoing in the past and were interrupted by a specific event (which is expressed in pretérito indefinido). For example: Hablaba por teléfono cuando alguien llamó a la puerta.
Regular Verbs:
To the verb root, we add the following endings:
-ar ➯ -aba, -abas, -aba, -ábamos, -abais, -aban.
-er/-ir ➯ -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían.
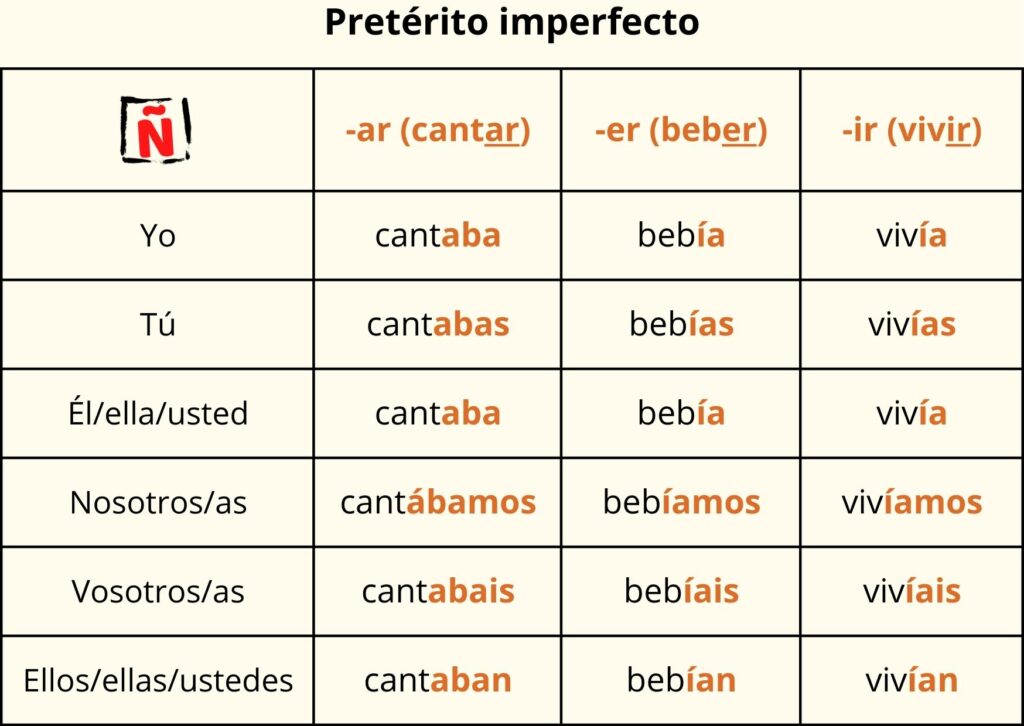
Irregular verbs:
In pretérito imperfecto, there are only three irregular verbs: ser, ir, and ver.
SER
Yo era
tú eras
él/ella/ud. era
nosotros/as éramos
vosotros/as erais
ellos/ellas/uds. eran
IR
Yo iba
tú ibas
él/ella/ud. iba
nosotros/as íbamos
vosotros/as ibais
ellos/ellas/uds. iban
ER
Yo veía
tú veías
él/ella/ud. veía
nosotros/as veíamos
vosotros/as veíais
ellos/ellas/uds. veían
Common Time Markers with Pretérito Imperfecto:
Antes, cuando tenía XX años, cuando era pequeño/a, cuando era joven, siempre, generalmente, a menudo, todos los años/meses/días…
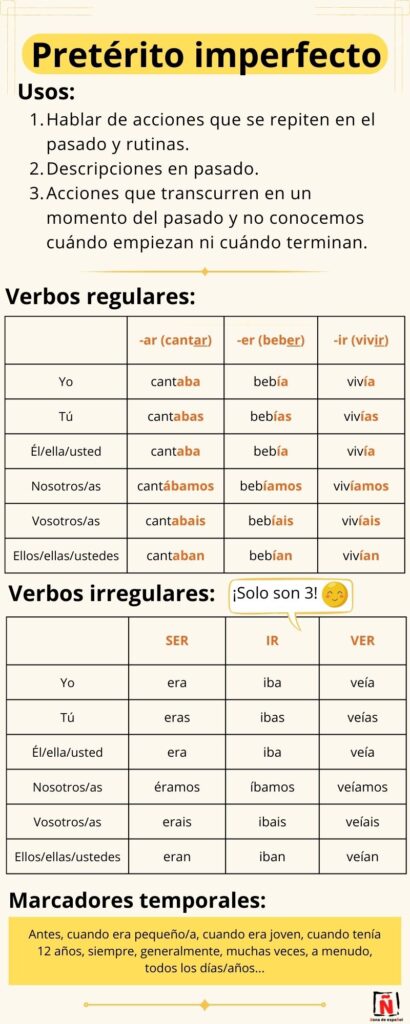
Here is the infographic that summarizes the entire explanation; you can find it in higher quality on our Facebook or Pinterest channel.
I hope you have liked this explanation. If you have any questions, you can leave a comment, and don’t forget to share this post with more people. 😊