Welcome to a new post in your Spanish corner! Today we are going to talk about the pretérito perfecto in Spanish, one of the verb tenses that generates the most questions among students.
The past tenses in Spanish are one of the grammatical points that students often have doubts about. That’s why we are going to explain each of the indicative past tenses in the coming days. Today, we start with the pretérito perfecto de indicativo (also called the pretérito perfecto compuesto).
What is the pretérito perfecto in Spanish used for?
1. To talk about past actions, whether completed or not, that are related to the present.
Example: Este año he trabajado mucho. (The year is not over, and this fact is connected to the present, which is why we use the pretérito perfecto).
2. To talk about personal experiences.
Example: He ido de acampada muchas veces con mis amigos.
3. To express actions without specifying exactly when they happened or when they ended.
Example: He tenido muchos problemas en casa. (We don’t know when that situation ended, which is why we use the Pretérito Perfecto).
The pretérito perfecto, or pretérito perfecto compuesto, is formed with the present of the verb “haber” (yo he, tu has, él ha, nosotros hemos, vosotros habéis, ellos han) and the past participle. For infinitive verbs ending in -ar, we add -ado to the verb root, and for verbs ending in -er or -ir, we add -ido.
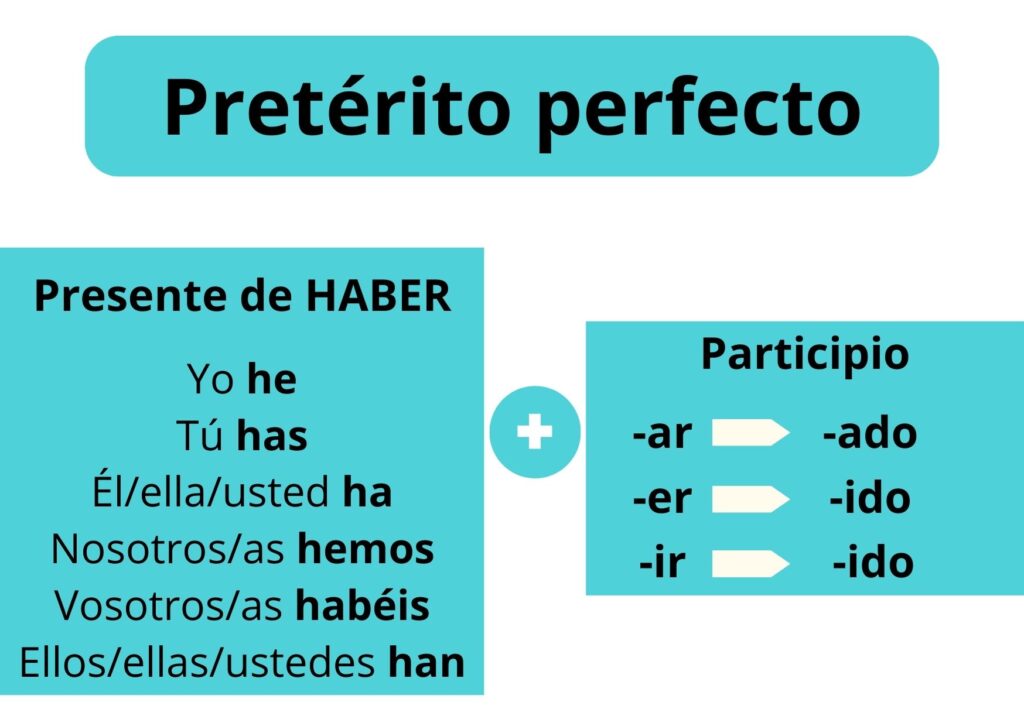
How is the past participle or Pretérito perfecto in Spanish formed?
The past participle in Spanish is formed by adding -ado or -ido to the root of the infinitive verb. Remember that the verb root is what you get when you remove -ar, -er, or -ir from the infinitive verb. For example: cantar, without -ar, we have cant- as the root of the verb.
To form the past participle, we need to remember two very simple rules:
- For verbs ending in -ar in the infinitive, the past participle ends in -ado.
- For verbs ending in -er or -ir in the infinitive, the past participle ends in -ido.
Examples:
Cantar –> cant- + –ado –> cantado
Comer –> com- + –ido –> comido
Vivir –> viv- + –ido –> vivido
Irregular participles:
The following participles are irregular. Derived verbs also have the irregular participle.
| Infinitive | Participle |
| hacer | hecho |
| romper | roto |
| ver | visto |
| poner | puesto |
| volver | vuelto |
| satisfacer | satisfecho |
| abrir | abierto |
| escribir | escrito |
| decir | dicho |
| morir | muerto |
| cubrir | cubierto |
| Participle of compound verbs | |
| devolver | devuelto |
| envolver | envuelto |
| resolver | resuelto |
| componer | compuesto |
| posponer | pospuesto |
| exponer | expuesto |
| deshacer | deshecho |
| descubrir | descubierto |
| suscribir | suscrito |
| encubrir | encubierto |
****Except: corromper –> corrompido (is regular) –> no “corroto“.
There are some participles that have two forms, one regular and one irregular. Both are correct and can be used interchangeably.
| Infinitive | Regular Participle | Irregular Participle |
| freír | freído | frito |
| imprimir | imprimido | |
| proveer | proveído | provisto |
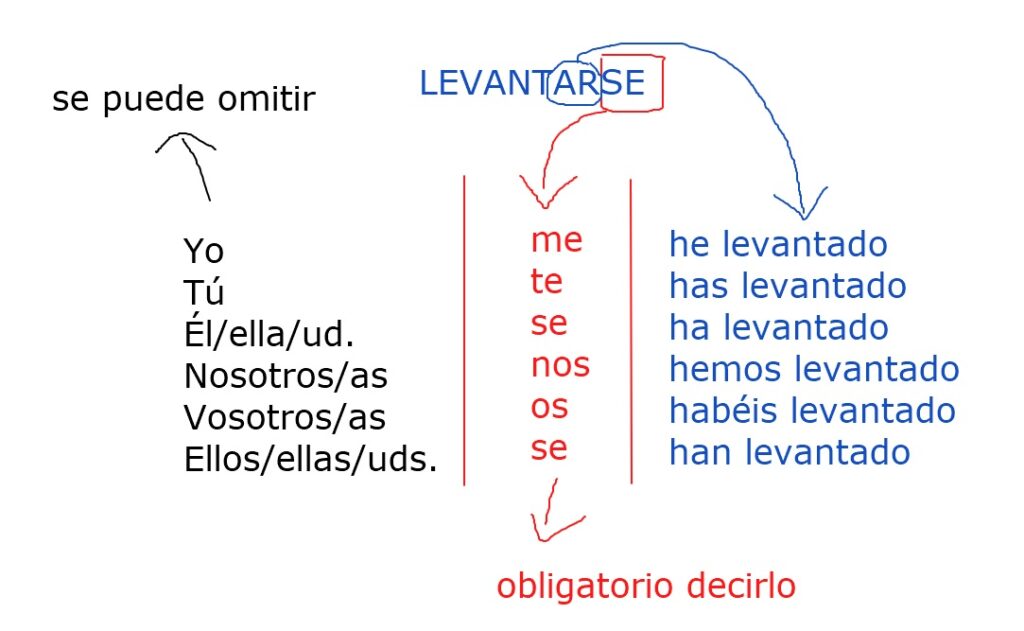
How is the pretérito perfecto with reflexive verbs?
If the verb is reflexive (-se), the reflexive pronoun (me, te, se, nos, os, se) is always placed before the verb “haber.”
Subject pronouns (yo, tú, él…) can be omitted, but we can never omit the reflexive pronoun (me, te, se…).
Markers in the pretérito perfecto tense:
The pretérito perfecto in Spanish is usually used with the following markers:
Hoy
Esta mañana/tarde/noche…
Este mes/año…
Estos días /recientemente/últimamente…
Siempre/nunca.
Ya/todavía no/ aún no
Here is an infographic that summarizes all the explanation today about the pretérito perfecto in Spanish.
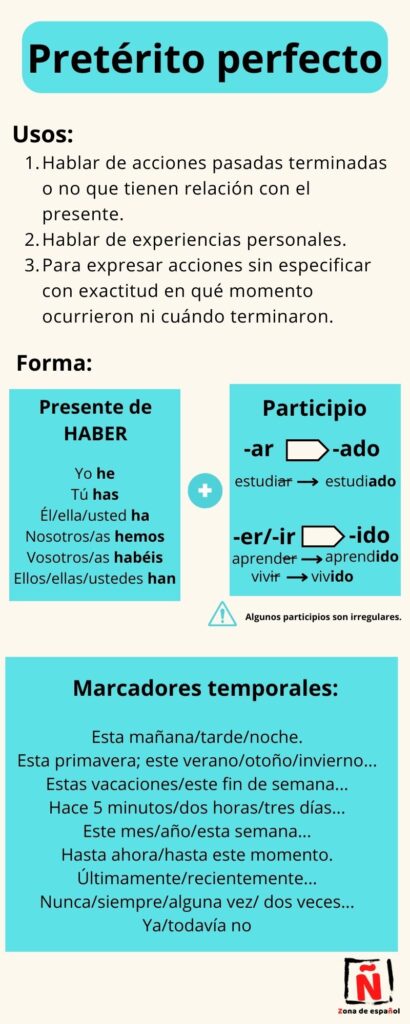
My advice as a teacher and as a language learner: you can print this infographic and stick it in your Spanish notebook. That way, you can always have it handy for reference. I would also write different example sentences in the notebook to know how to use the pretérito perfecto.
Do you have a clearer understanding of the present perfect now?
I hope today’s explanation and the infographic are helpful. In the next post, we will review the pretérito indefinido (simple past) tense.
Don’t forget to share this post, and if you have any questions, you can leave a comment. I will respond as soon as possible. And also, follow us on Instagram for more tips, resources, and fun ways to learn Spanish. Stay connected with Zona de Español: Instagram
Would you like to learn more about how to use the present perfect in Spanish fluently and naturally? Join our online Spanish course at Zona de Español and improve your language skills with our dynamic and interactive classes. Sign up now and start speaking Spanish with confidence!